Copilot for SQL Server database in Microsoft Fabric
Introduction to Copilot for SQL Server database
Copilot for SQL database utilizes table and view names, column names, primary key, and foreign key metadata to generate T-SQL code. Copilot for SQL database does not use data in tables to generate T-SQL suggestions.
Developers can ask natural language questions about their data to generate T-SQL queries or rely on Copilot to complete their code as they type.
Database administrators can optimize their queries or troubleshoot errors, with Copilot providing solutions and insights directly in response to error messages
Key features of Copilot for SQL database include:
Code completion: Start writing T-SQL in the SQL query editor and Copilot will automatically generate a code suggestion to help complete your query. The Tab key accepts the code suggestion or keeps typing to ignore the suggestion.
Quick actions: In the ribbon of the SQL query editor, the Fix and Explain options are quick actions. Highlight a SQL query of your choice and select one of the quick action buttons to perform the selected action on your query.
Fix: Copilot can fix errors in your code as error messages arise. Error scenarios can include incorrect/unsupported T-SQL code, wrong spellings, and more. Copilot will also provide comments that explain the changes and suggest SQL best practices.
Explain: Copilot can provide natural language explanations of your SQL query and database schema in comments format.
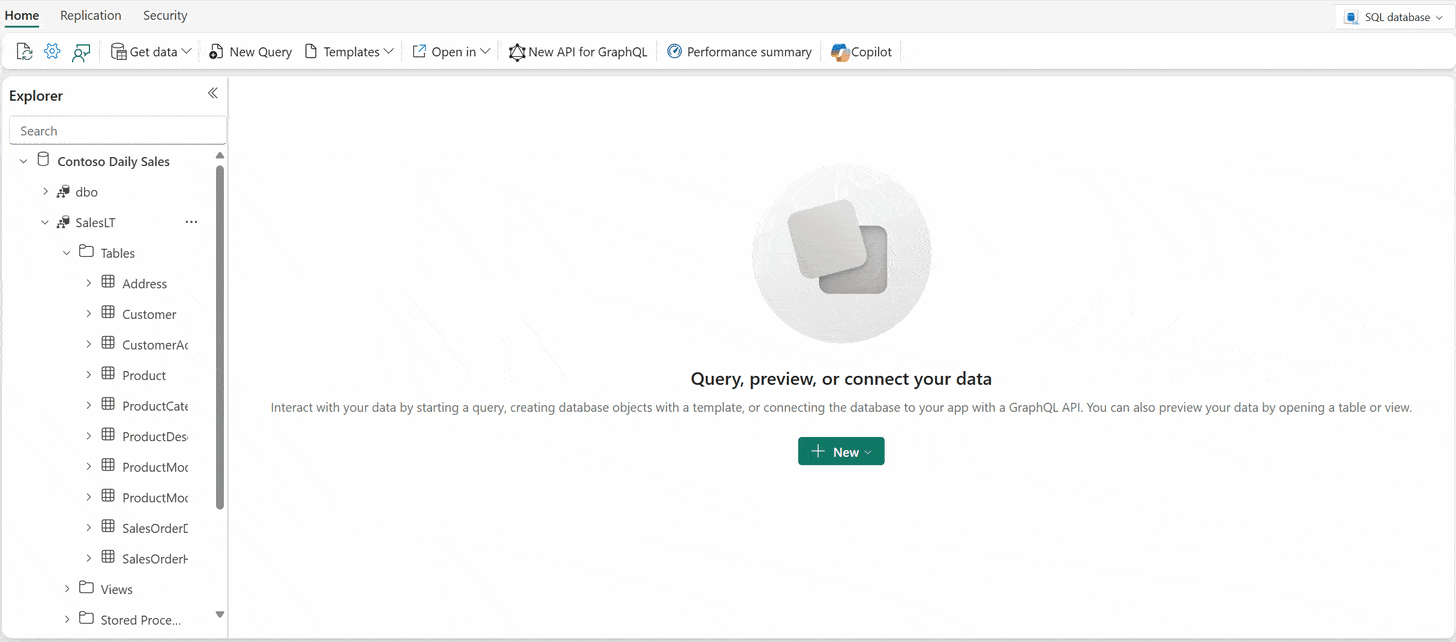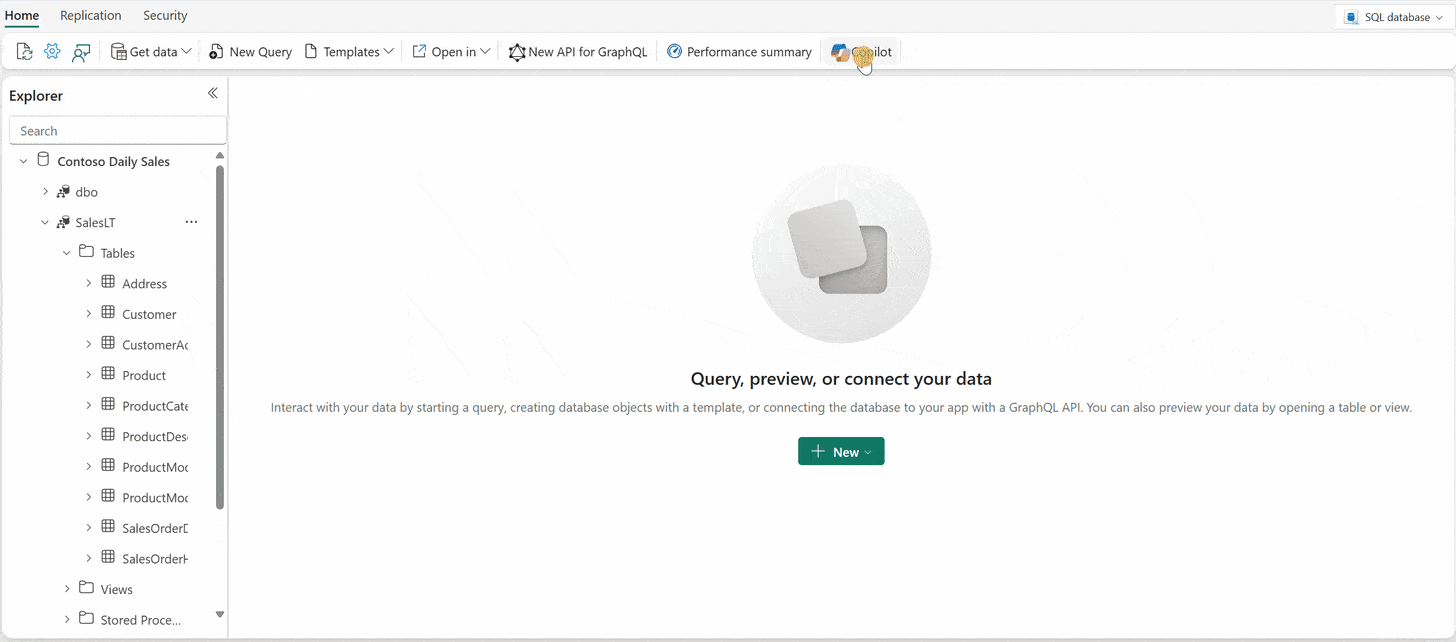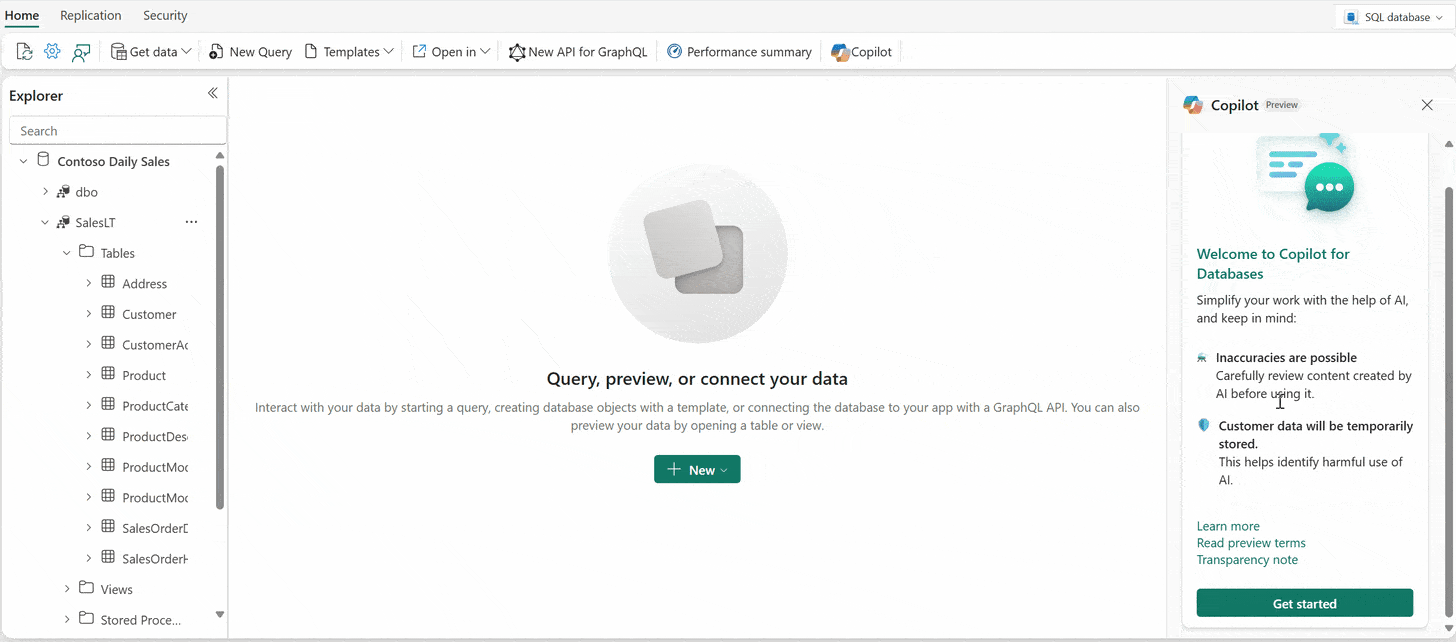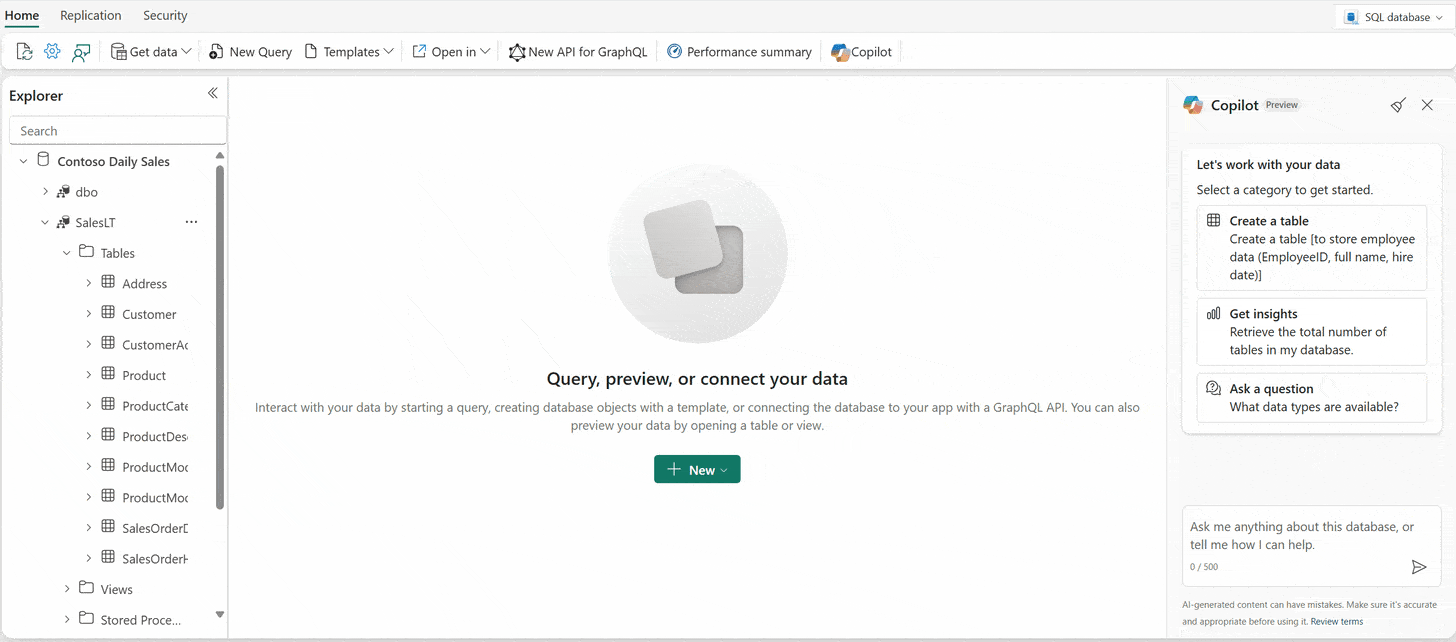
Chat pane: Use the chat pane to ask questions to Copilot through natural language. Copilot responds with a generated SQL query or natural language based on the question asked.
Natural Language to SQL: Generate T-SQL code from plain text requests, allowing users to query data without needing to know SQL syntax.
Document-based Q&A: Ask Copilot questions about general SQL database capabilities, and it responds in natural language. Copilot also helps find documentation related to your request.
Natural language to SQL conversion
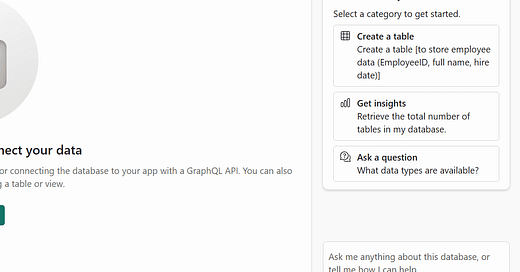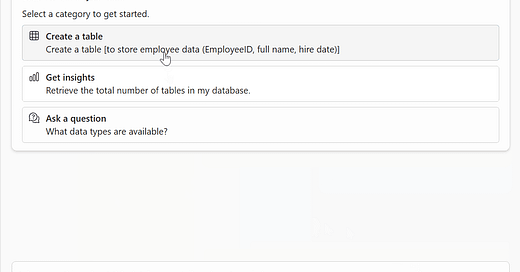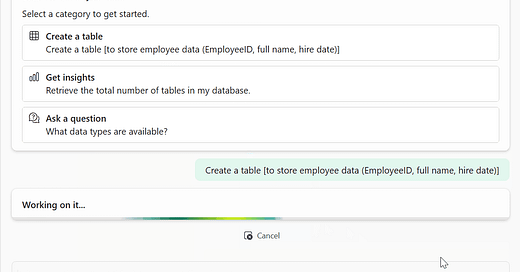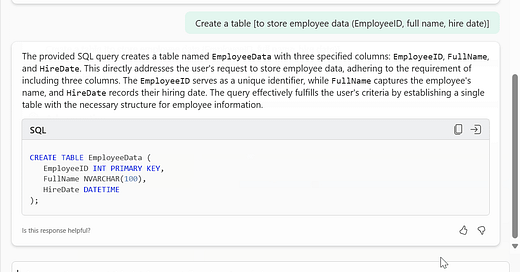
Copilot can generate DML/DDL/DQL code based on user requests, enabling seamless data querying or object creation.
Sample prompts:
“Create a table called SalesTransactions with columns named CustomerID, ProductID, OrderDate, Quantity”
“Show customers who placed an order in 2024 and haven’t placed another since.”
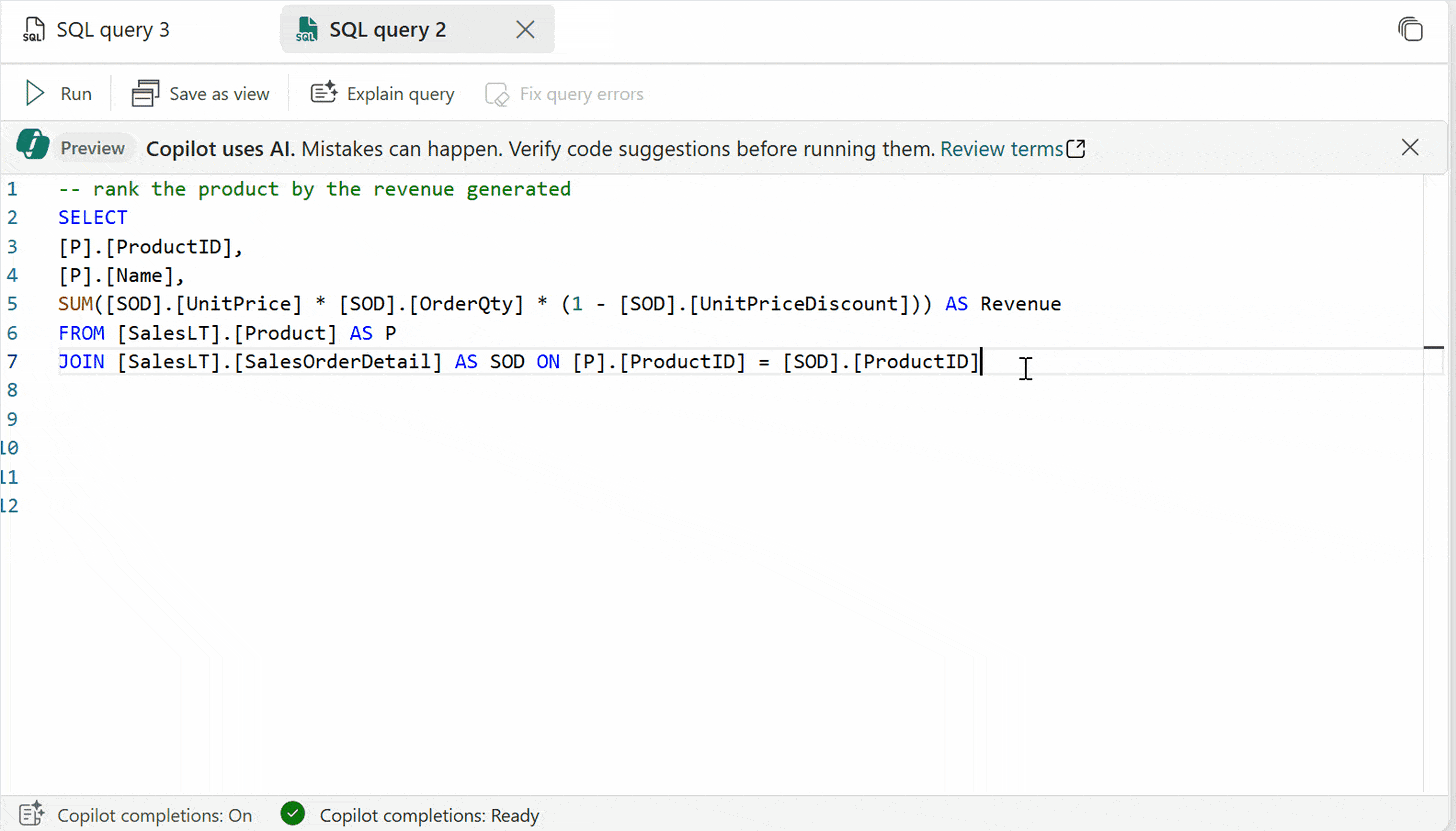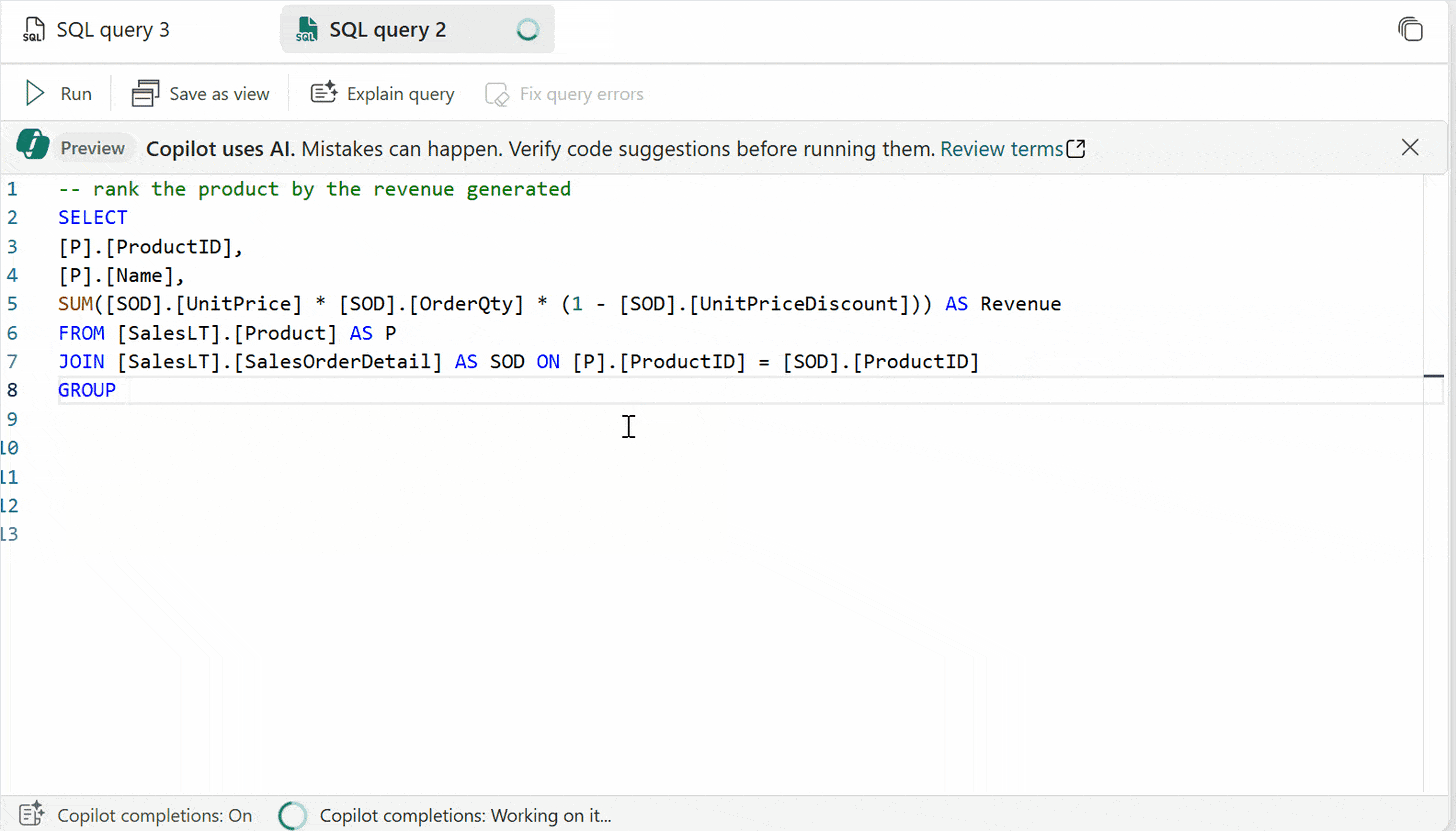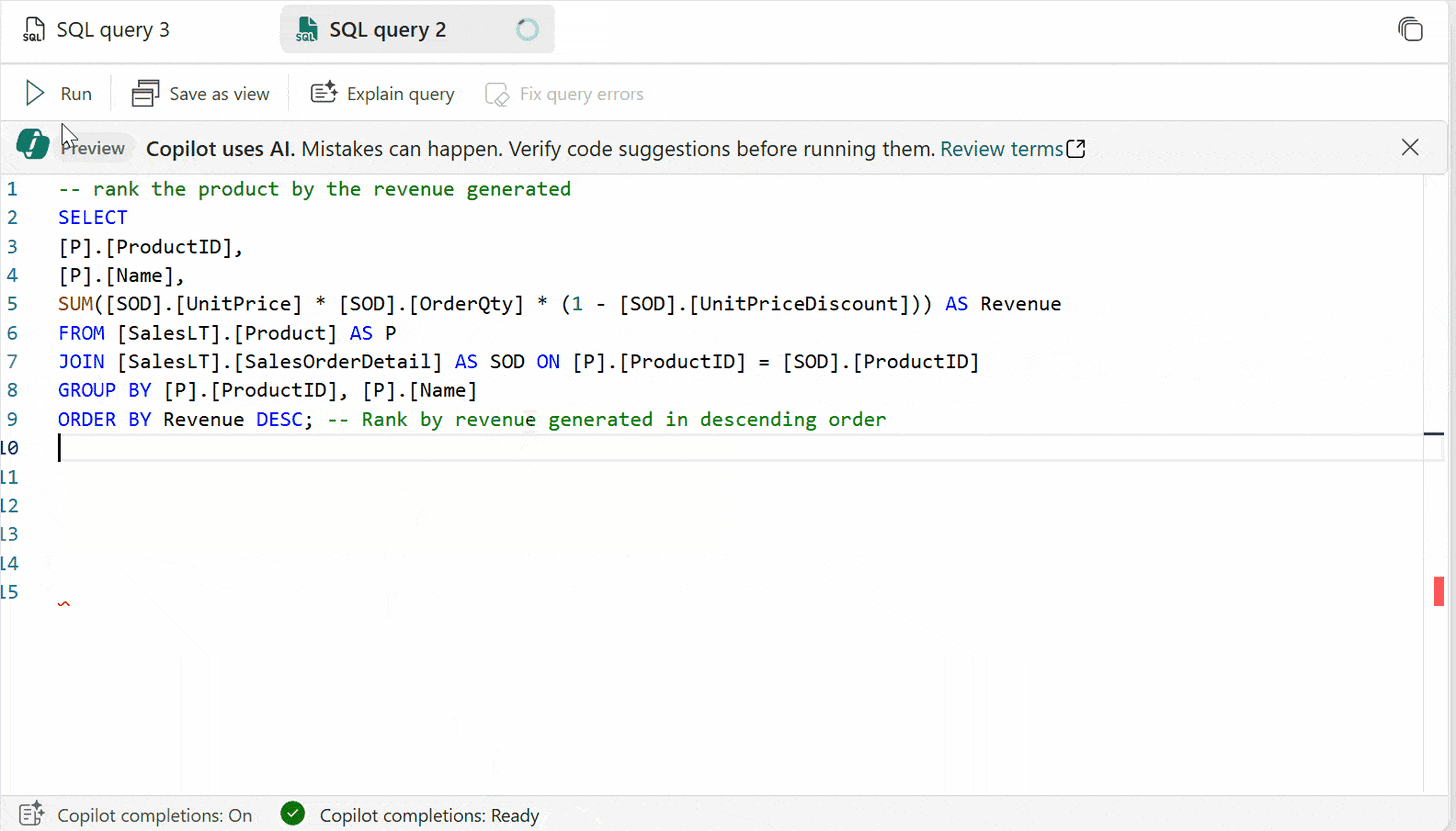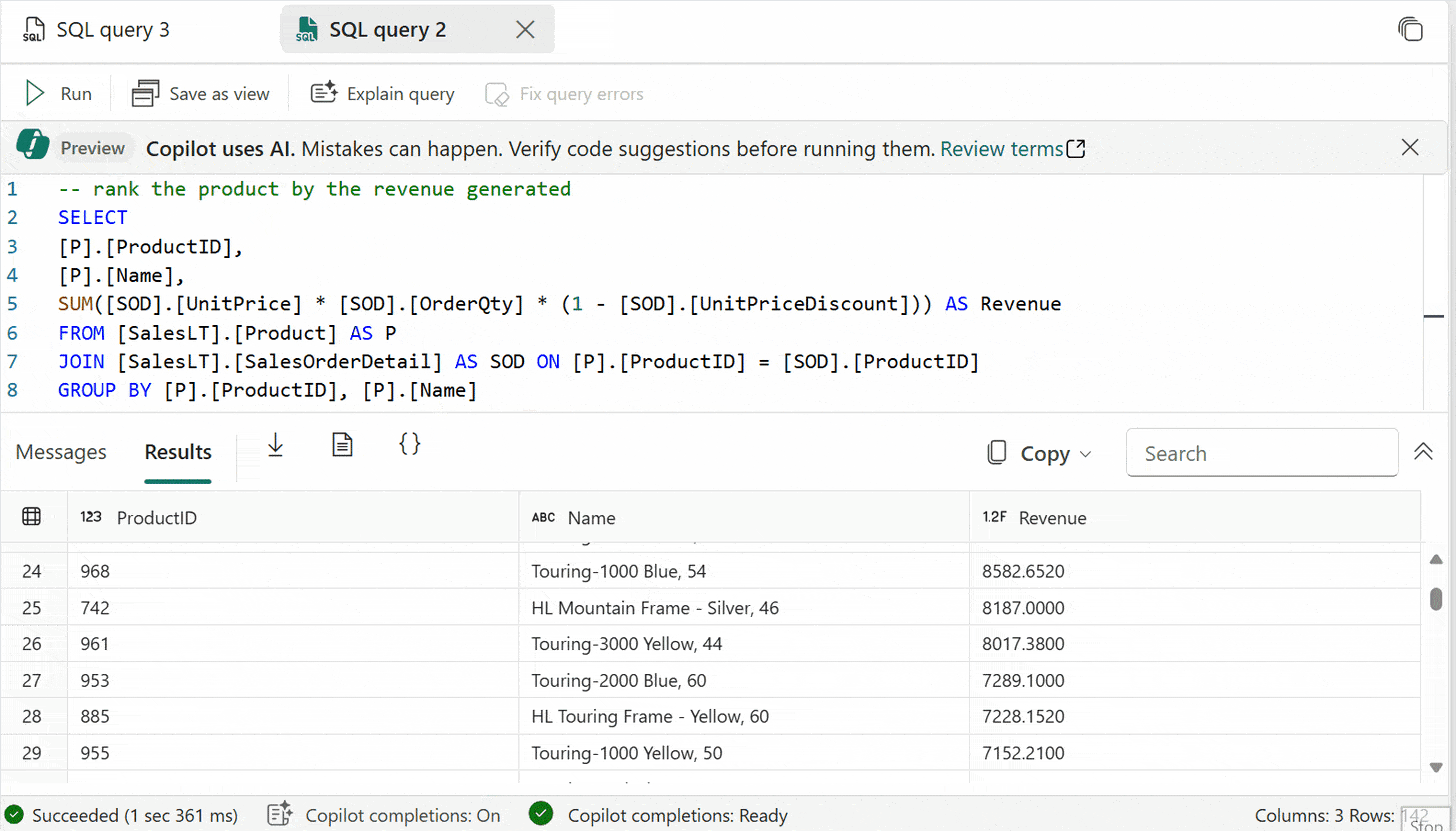
“Rank employees by their sales performance in each region.
Document-Based Insights
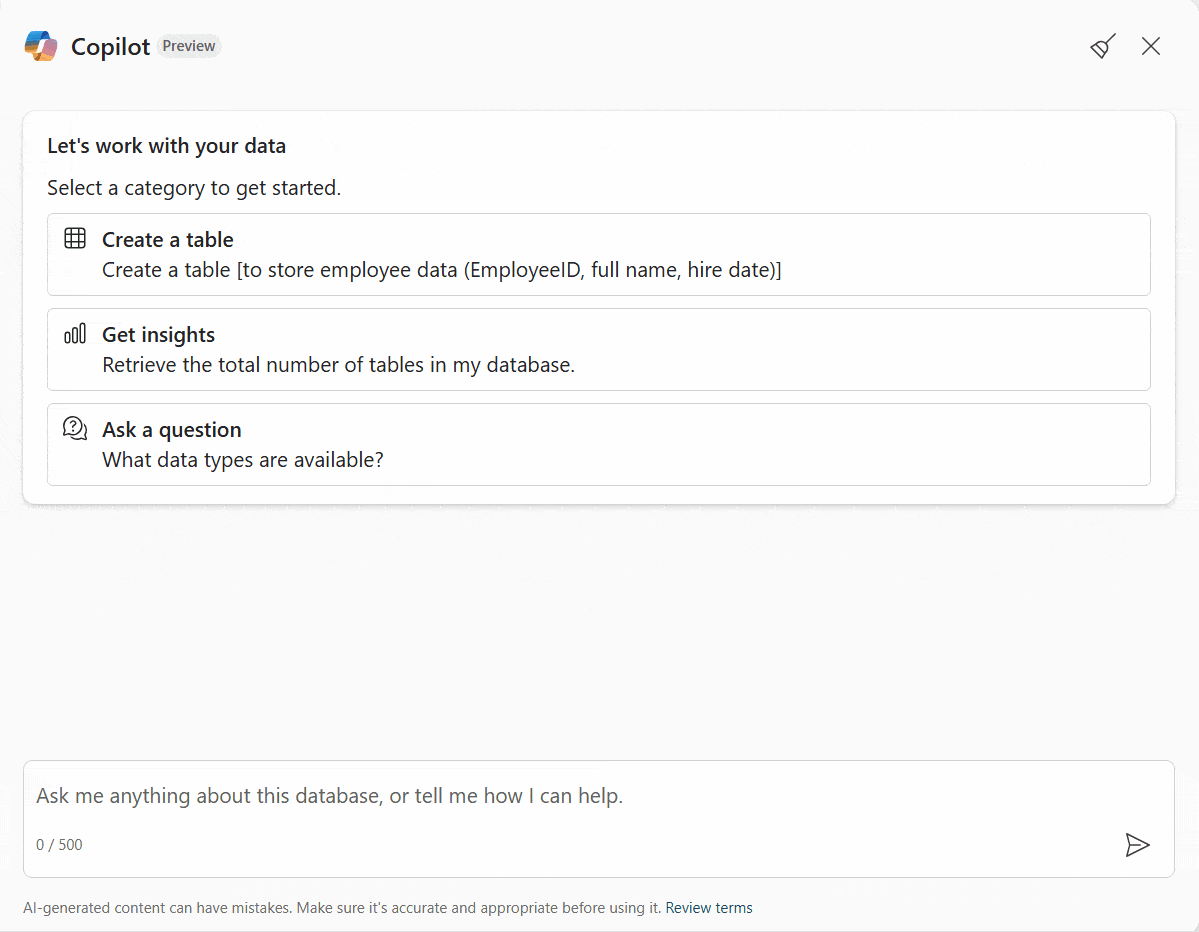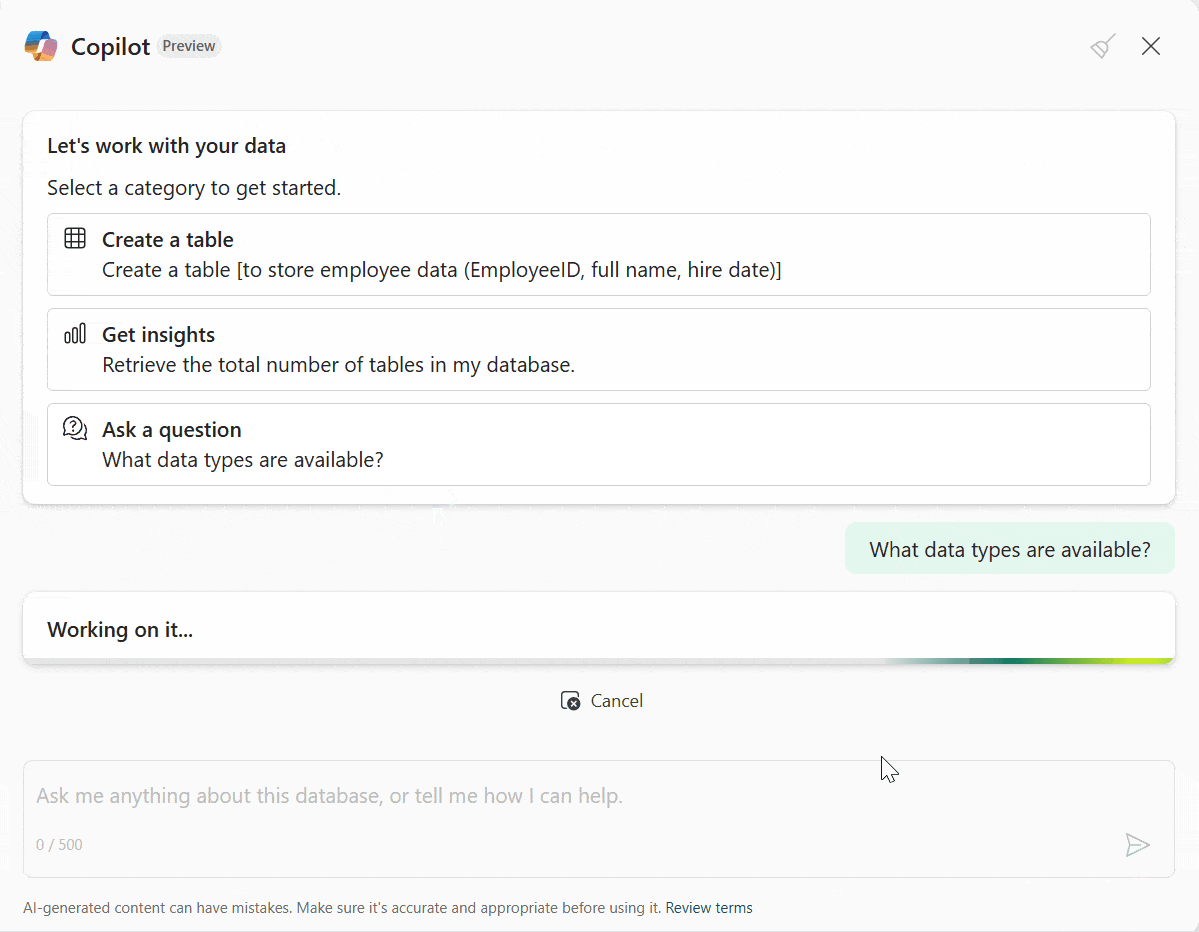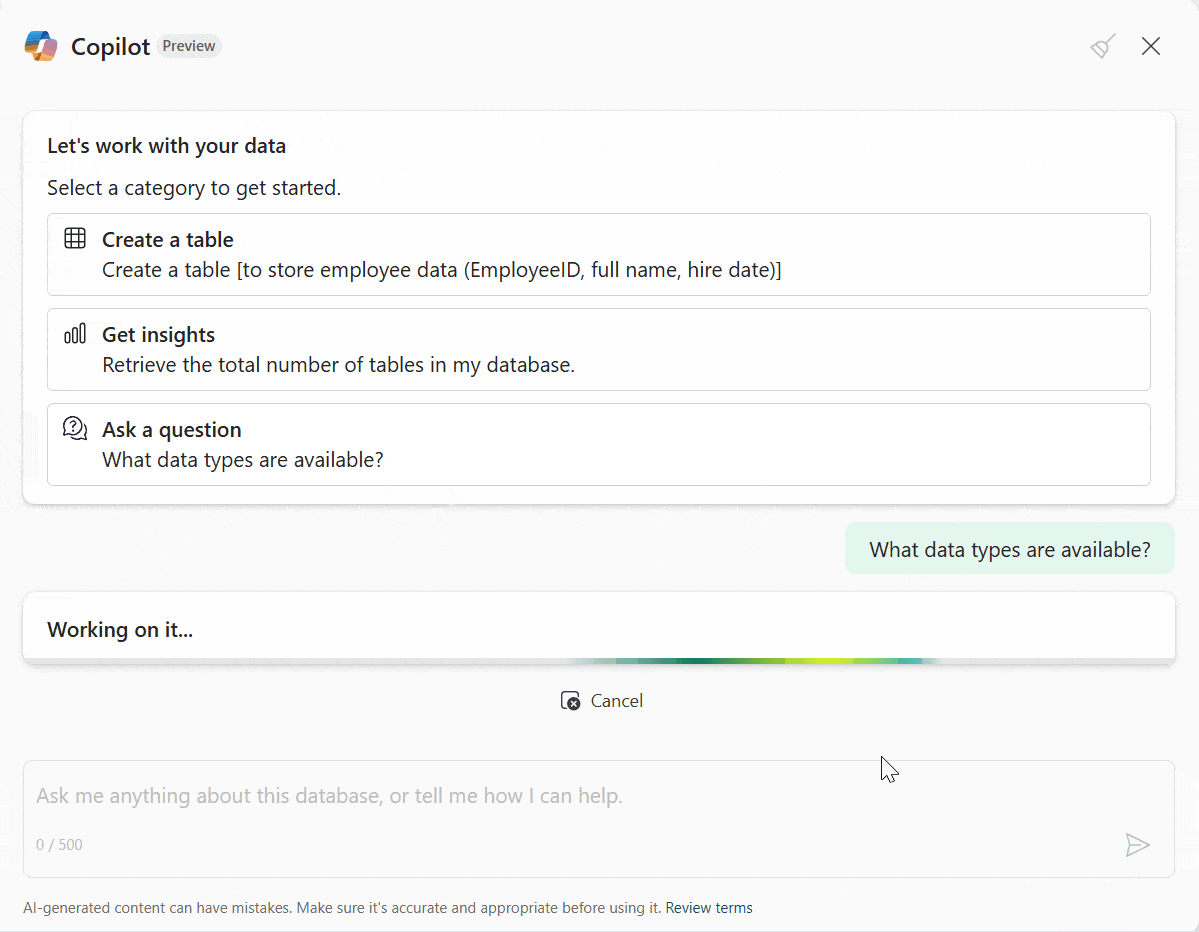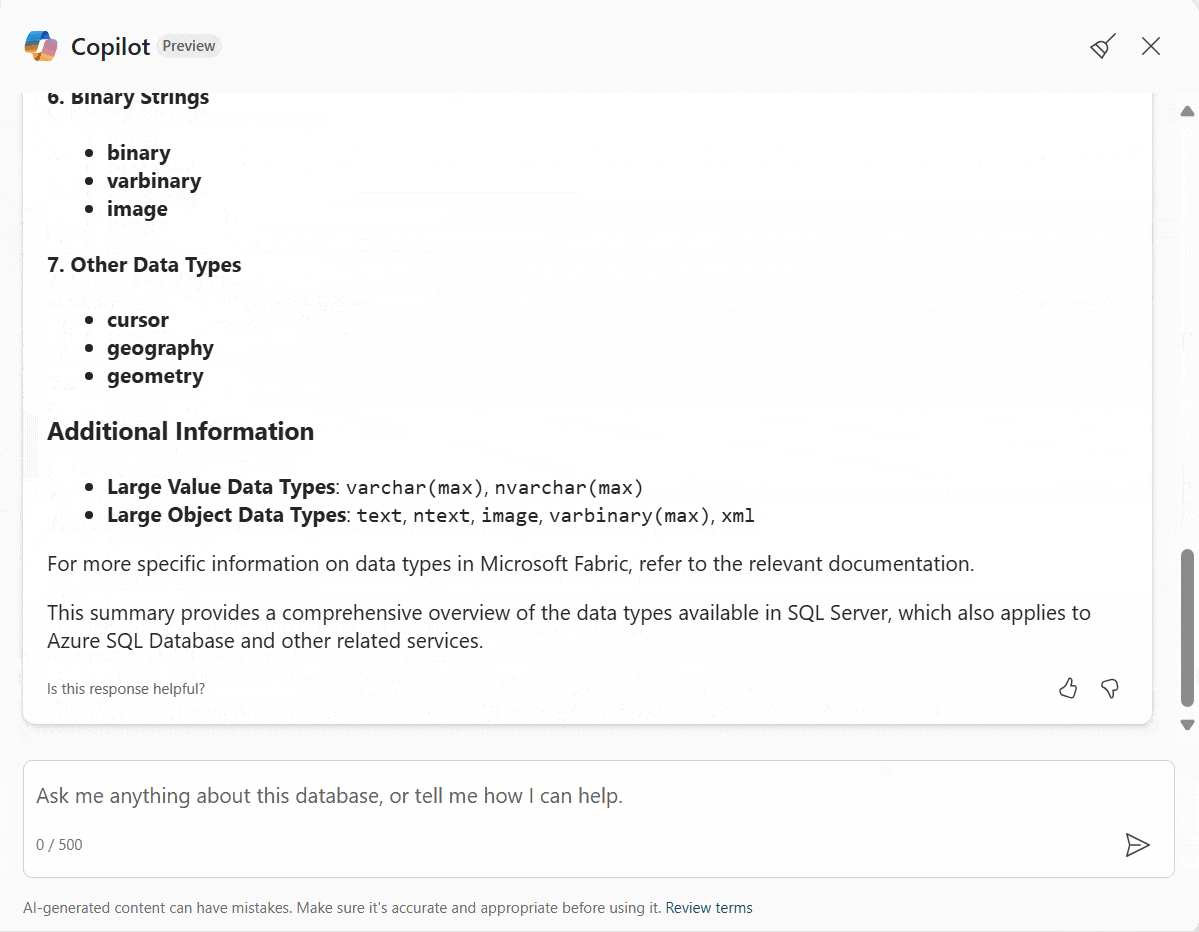
Ask Copilot questions about general SQL database capabilities, such as standard SQL language, query processing, and database management features, and copilot will provide an answer based on relevant Microsoft Learn documentation.
Sample prompts:
“What data types are available?”
“How does my database auto-scale?”
“How do I query from two or more tables?”
Inline Code Completion: Write Faster, Cleaner SQL
Copilot generates real-time code suggestions to help you complete your code faster. This feature reduces the need to constantly switch between your editor and external resources like documentation or search engines. It also minimizes common syntax errors, leading to cleaner and more reliable code.
Fix Code Error and Explain query
Fix Code error feature quickly identifies coding errors and suggests fixes, allowing you to maintain your workflow without interruption. It minimizes the risk of introducing new errors by providing fixes that are contextualized to your schema.
Explain query feature provides clear, detailed explanations of complex code, making it an excellent learning tool for both new and experienced SQL users. It also promotes better communication and understanding within teams, enhancing collaboration.
Limitations of Copilot for SQL database
Here are the current limitations of Copilot for SQL database:
Copilot can't make changes to existing SQL queries in the SQL query editor. For example, if you ask Copilot chat pane to edit a specific part of an existing query, it doesn't work. However, Copilot understands previous inputs in the chat pane, allowing users to iterate queries previously generated by Copilot before they're inserted.
Copilot might produce inaccurate results when the intent is to evaluate data. Copilot only has access to the database schema, none of the data inside.
Copilot responses can include inaccurate or low-quality content, so make sure to review outputs before using them in your work.